Magnesium »
PDB 1eo3-1f6t »
1f51 »
Magnesium in PDB 1f51: A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction
Protein crystallography data
The structure of A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction, PDB code: 1f51
was solved by
J.Zapf,
U.Sen,
M.Madhusudan,
J.A.Hoch,
K.I.Varughese,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 45.00 / 3.00 |
| Space group | P 21 21 21 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 72.974, 117.774, 170.736, 90.00, 90.00, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 22.8 / 26.8 |
Magnesium Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Magnesium atom in the A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction
(pdb code 1f51). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Magnesium atom.
In total 3 binding sites of Magnesium where determined in the A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction, PDB code: 1f51:
Jump to Magnesium binding site number: 1; 2; 3;
In total 3 binding sites of Magnesium where determined in the A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction, PDB code: 1f51:
Jump to Magnesium binding site number: 1; 2; 3;
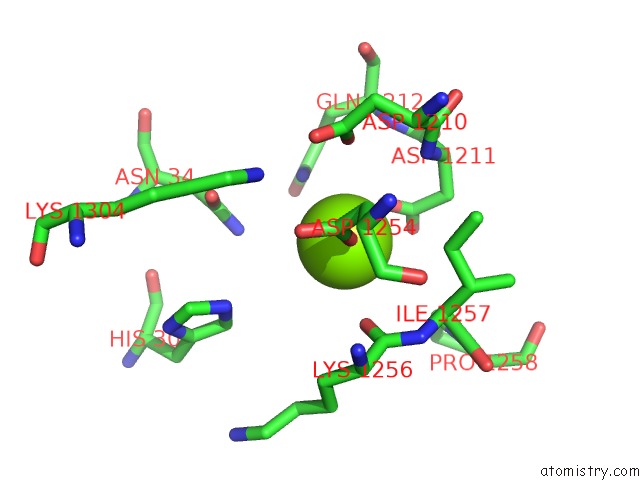
Magnesium binding site 1 out of 3 in 1f51
Go back to
Magnesium binding site 1 out
of 3 in the A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction
Mono view

Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Magnesium with other atoms in the Mg binding
site number 1 of A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction within 5.0Å range:
|
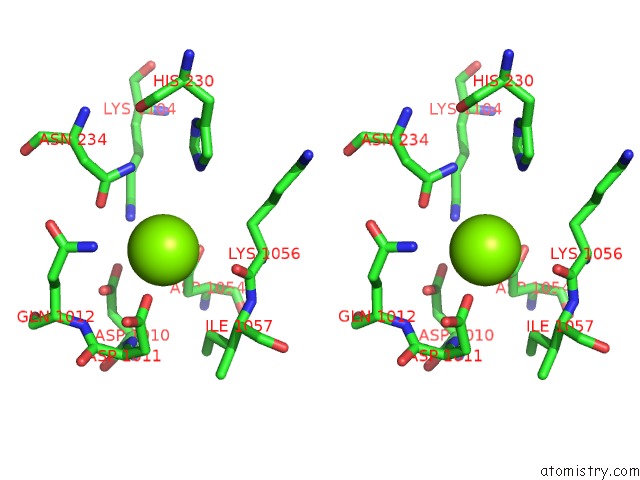
Magnesium binding site 2 out of 3 in 1f51
Go back to
Magnesium binding site 2 out
of 3 in the A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction

Mono view
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Magnesium with other atoms in the Mg binding
site number 2 of A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction within 5.0Å range:
|
Magnesium binding site 3 out of 3 in 1f51
Go back to
Magnesium binding site 3 out
of 3 in the A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction

Mono view

Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Magnesium with other atoms in the Mg binding
site number 3 of A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Singal Transduction within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
J.Zapf,
U.Sen,
M.Madhusudan,
J.A.Hoch,
K.I.Varughese.
A Transient Interaction Between Two Phosphorelay Proteins Trapped in A Crystal Lattice Reveals the Mechanism of Molecular Recognition and Phosphotransfer in Signal Transduction. Structure Fold.Des. V. 8 851 2000.
ISSN: ISSN 0969-2126
PubMed: 10997904
DOI: 10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00174-X
Page generated: Tue Aug 13 03:07:27 2024
ISSN: ISSN 0969-2126
PubMed: 10997904
DOI: 10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00174-X
Last articles
F in 7KYAF in 7KY5
F in 7KXW
F in 7KY9
F in 7KWA
F in 7KXT
F in 7KXC
F in 7KWV
F in 7KXL
F in 7KW4