Magnesium »
PDB 3fps-3fzi »
3frg »
Magnesium in PDB 3frg: Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor
Enzymatic activity of Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor
All present enzymatic activity of Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor:
3.1.4.17;
3.1.4.17;
Protein crystallography data
The structure of Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor, PDB code: 3frg
was solved by
D.O.Somers,
M.Neu,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 20.00 / 1.70 |
| Space group | I 21 21 21 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 88.485, 94.831, 105.320, 90.00, 90.00, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 20.9 / 24.2 |
Other elements in 3frg:
The structure of Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor also contains other interesting chemical elements:
| Arsenic | (As) | 4 atoms |
| Zinc | (Zn) | 1 atom |
Magnesium Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Magnesium atom in the Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor
(pdb code 3frg). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Magnesium atom.
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor, PDB code: 3frg:
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor, PDB code: 3frg:
Magnesium binding site 1 out of 1 in 3frg
Go back to
Magnesium binding site 1 out
of 1 in the Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor
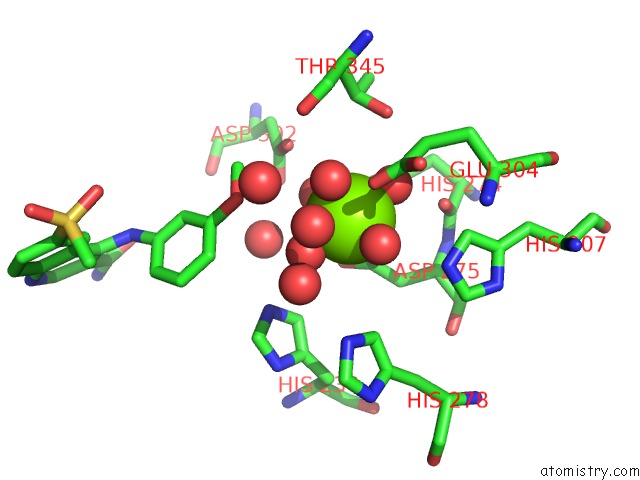
Mono view
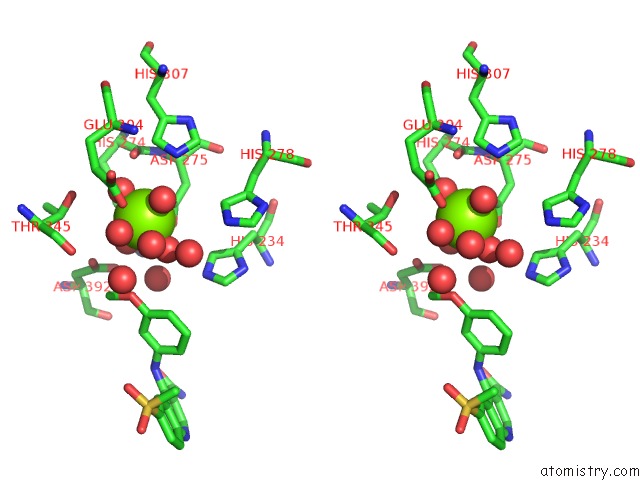
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Magnesium with other atoms in the Mg binding
site number 1 of Catalytic Domain of Human Phosphodiesterase 4B2B in Complex with A Quinoline Inhibitor within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
C.J.Lunniss,
A.W.Cooper,
C.D.Eldred,
M.Kranz,
M.Lindvall,
F.S.Lucas,
M.Neu,
A.G.Preston,
L.E.Ranshaw,
A.J.Redgrave,
J.Ed Robinson,
T.J.Shipley,
Y.E.Solanke,
D.O.Somers,
J.O.Wiseman.
Quinolines As A Novel Structural Class of Potent and Selective PDE4 Inhibitors: Optimisation For Oral Administration. Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett. V. 19 1380 2009.
ISSN: ISSN 0960-894X
PubMed: 19195882
DOI: 10.1016/J.BMCL.2009.01.045
Page generated: Wed Aug 14 13:52:44 2024
ISSN: ISSN 0960-894X
PubMed: 19195882
DOI: 10.1016/J.BMCL.2009.01.045
Last articles
Zn in 9J0NZn in 9J0O
Zn in 9J0P
Zn in 9FJX
Zn in 9EKB
Zn in 9C0F
Zn in 9CAH
Zn in 9CH0
Zn in 9CH3
Zn in 9CH1