Magnesium »
PDB 4ix4-4j9k »
4j96 »
Magnesium in PDB 4j96: Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer.
Enzymatic activity of Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer.
All present enzymatic activity of Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer.:
2.7.10.1;
2.7.10.1;
Protein crystallography data
The structure of Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer., PDB code: 4j96
was solved by
H.Chen,
M.Mohammadi,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 47.55 / 2.30 |
| Space group | P 43 2 2 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 73.852, 73.852, 310.716, 90.00, 90.00, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 17.6 / 21.9 |
Magnesium Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Magnesium atom in the Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer.
(pdb code 4j96). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Magnesium atom.
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer., PDB code: 4j96:
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer., PDB code: 4j96:
Magnesium binding site 1 out of 1 in 4j96
Go back to
Magnesium binding site 1 out
of 1 in the Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer.
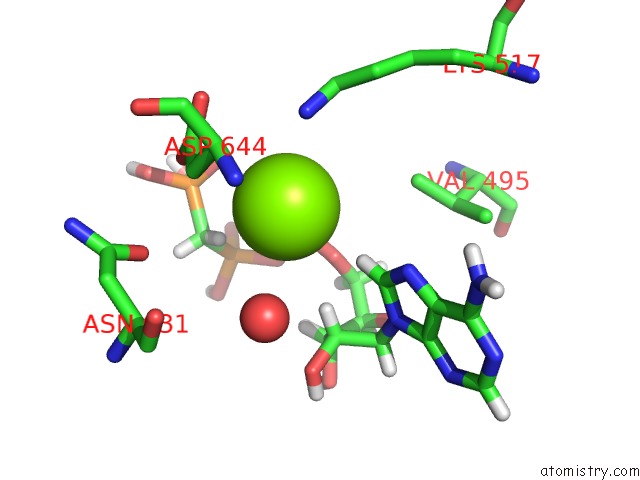
Mono view
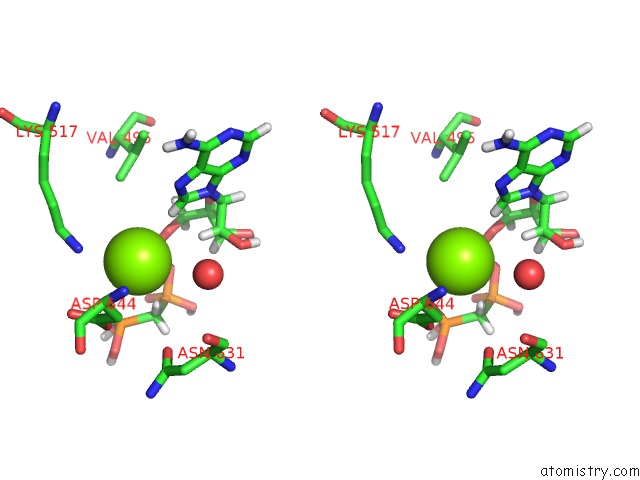
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Magnesium with other atoms in the Mg binding
site number 1 of Crystal Structure of Fgf Receptor 2 (FGFR2) Kinase Domain Harboring the Pathogenic Gain-of-Function K659M Mutation Identified in Cervical Cancer. within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
H.Chen,
Z.Huang,
K.Dutta,
S.Blais,
T.A.Neubert,
X.Li,
D.Cowburn,
N.J.Traaseth,
M.Mohammadi.
Cracking the Molecular Origin of Intrinsic Tyrosine Kinase Activity Through Analysis of Pathogenic Gain-of-Function Mutations. Cell Rep V. 4 376 2013.
ISSN: ESSN 2211-1247
PubMed: 23871672
DOI: 10.1016/J.CELREP.2013.06.025
Page generated: Mon Aug 11 14:37:04 2025
ISSN: ESSN 2211-1247
PubMed: 23871672
DOI: 10.1016/J.CELREP.2013.06.025
Last articles
Mg in 4LNLMg in 4LNJ
Mg in 4LND
Mg in 4LNC
Mg in 4LN7
Mg in 4LMN
Mg in 4LLY
Mg in 4LLG
Mg in 4LK1
Mg in 4LK0