Magnesium »
PDB 5d2k-5dar »
5d9d »
Magnesium in PDB 5d9d: Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature
Protein crystallography data
The structure of Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature, PDB code: 5d9d
was solved by
K.Yamashita,
D.Pan,
T.Okuda,
T.Murai,
A.Kodan,
T.Yamaguchi,
K.Gomi,
N.Kajiyama,
H.Kato,
H.Ago,
M.Yamamoto,
T.Nakatsu,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 41.86 / 1.70 |
| Space group | P 21 21 21 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 48.107, 77.177, 84.916, 90.00, 90.00, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 14.4 / 17.8 |
Other elements in 5d9d:
The structure of Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature also contains other interesting chemical elements:
| Mercury | (Hg) | 3 atoms |
Magnesium Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Magnesium atom in the Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature
(pdb code 5d9d). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Magnesium atom.
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature, PDB code: 5d9d:
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature, PDB code: 5d9d:
Magnesium binding site 1 out of 1 in 5d9d
Go back to
Magnesium binding site 1 out
of 1 in the Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature
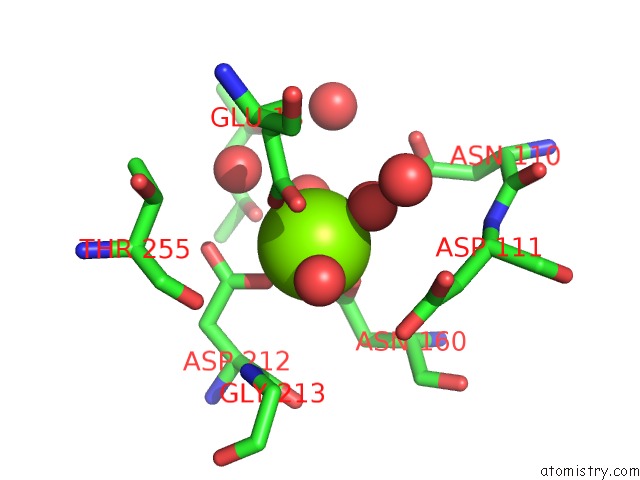
Mono view
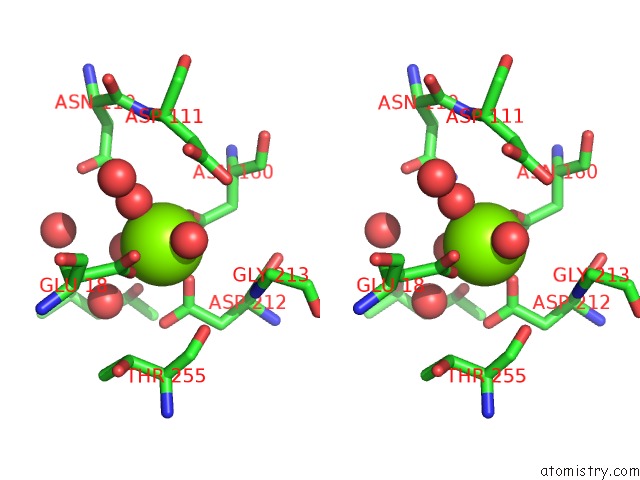
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Magnesium with other atoms in the Mg binding
site number 1 of Luciferin-Regenerating Enzyme Solved By Sad Using Synchrotron Radiation at Room Temperature within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
K.Yamashita,
D.Pan,
T.Okuda,
M.Sugahara,
A.Kodan,
T.Yamaguchi,
T.Murai,
K.Gomi,
N.Kajiyama,
E.Mizohata,
M.Suzuki,
E.Nango,
K.Tono,
Y.Joti,
T.Kameshima,
J.Park,
C.Song,
T.Hatsui,
M.Yabashi,
S.Iwata,
H.Kato,
H.Ago,
M.Yamamoto,
T.Nakatsu.
An Isomorphous Replacement Method For Efficient De Novo Phasing For Serial Femtosecond Crystallography. Sci Rep V. 5 14017 2015.
ISSN: ESSN 2045-2322
PubMed: 26360462
DOI: 10.1038/SREP14017
Page generated: Sun Sep 29 02:38:59 2024
ISSN: ESSN 2045-2322
PubMed: 26360462
DOI: 10.1038/SREP14017
Last articles
Zn in 9MJ5Zn in 9HNW
Zn in 9G0L
Zn in 9FNE
Zn in 9DZN
Zn in 9E0I
Zn in 9D32
Zn in 9DAK
Zn in 8ZXC
Zn in 8ZUF