Magnesium »
PDB 6rux-6s40 »
6s2j »
Magnesium in PDB 6s2j: Square Conformation of Ktra R16K Mutant Ring with Bound Atp
Protein crystallography data
The structure of Square Conformation of Ktra R16K Mutant Ring with Bound Atp, PDB code: 6s2j
was solved by
C.M.Teixeira-Duarte,
F.Fonseca,
J.H.Morais-Cabral,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 46.17 / 2.67 |
| Space group | I 4 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 123.276, 123.276, 84.451, 90.00, 90.00, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 19 / 23.6 |
Magnesium Binding Sites:
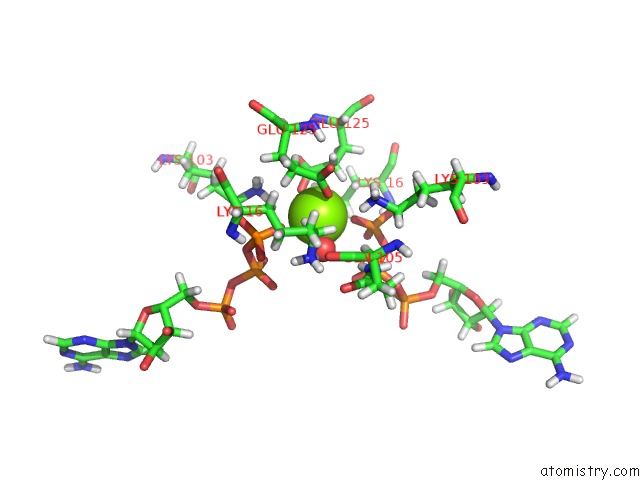
The binding sites of Magnesium atom in the Square Conformation of Ktra R16K Mutant Ring with Bound Atp
(pdb code 6s2j). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Magnesium atom.
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Square Conformation of Ktra R16K Mutant Ring with Bound Atp, PDB code: 6s2j:
In total only one binding site of Magnesium was determined in the Square Conformation of Ktra R16K Mutant Ring with Bound Atp, PDB code: 6s2j:
Magnesium binding site 1 out of 1 in 6s2j
Go back to
Magnesium binding site 1 out
of 1 in the Square Conformation of Ktra R16K Mutant Ring with Bound Atp
Mono view

Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Magnesium with other atoms in the Mg binding
site number 1 of Square Conformation of Ktra R16K Mutant Ring with Bound Atp within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
C.M.Teixeira-Duarte,
F.Fonseca,
J.H.Morais Cabral.
Activation of A Nucleotide-Dependent Rck Domain Requires Binding of A Cation Cofactor to A Conserved Site. Elife V. 8 2019.
ISSN: ESSN 2050-084X
PubMed: 31868587
DOI: 10.7554/ELIFE.50661
Page generated: Tue Oct 1 17:36:37 2024
ISSN: ESSN 2050-084X
PubMed: 31868587
DOI: 10.7554/ELIFE.50661
Last articles
Zn in 9JYWZn in 9IR4
Zn in 9IR3
Zn in 9GMX
Zn in 9GMW
Zn in 9JEJ
Zn in 9ERF
Zn in 9ERE
Zn in 9EGV
Zn in 9EGW